Bronze is widely researched in the fields of society science, historical archaeology, and nature geography. What is less widely recognized is that it also makes a significant contribution to industrial manufacturing.
This article aims to elucidate the enigma surrounding this particular alloy.
What is Bronze?
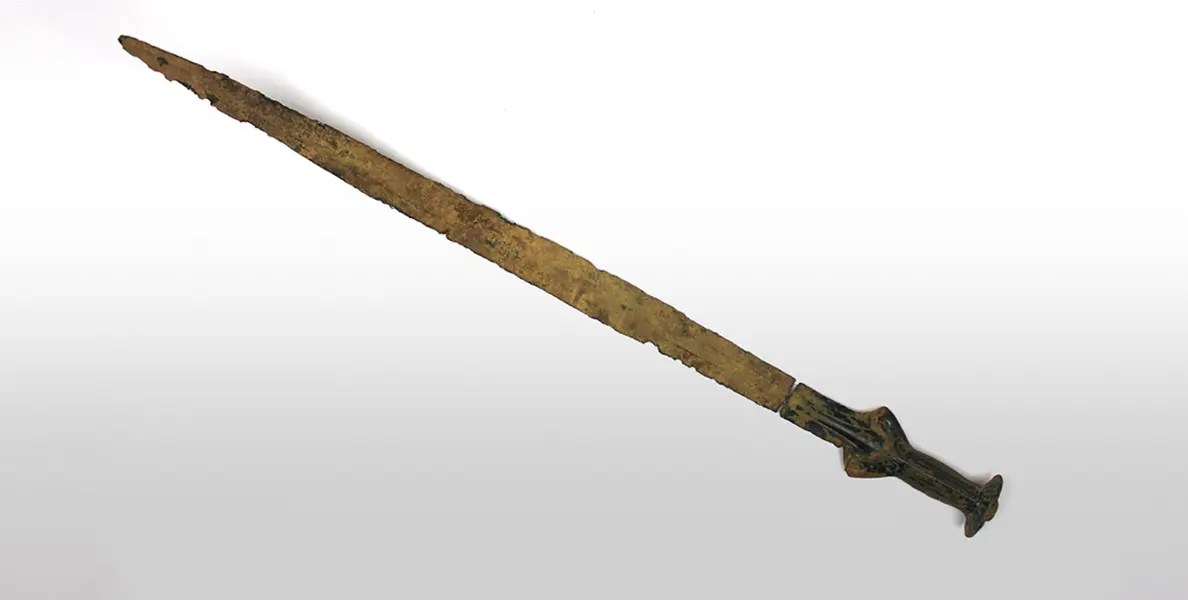

In this part, I’ll introduce you to bronze’s definition, history, composition, and properties.
Definition of Bronze
Bronze is a copper alloy consisting of copper and tin. The proportion of tin to copper can affect the properties of the bronze, with higher tin content resulting in a harder and more brittle alloy.
It has been used for thousands of years for various applications, including tools, weapons, sculptures, and musical instruments.
History of Bronze
Bronze is an alloy used since the early stage of human civilization.
The Bronze Age is known as the second period of the three-age system, together with the Stone Age and the Iron Age.
This is a period in prehistory characterized by the widespread use of bronze. In the Near East, it began around 3000 BCE and slowly spread to other parts of the world.
Due to copper’s ease of processing, this alloy of copper and tin was the first metal alloy created by humans. The development of bronze and copper casting marked a significant advancement in metalworking.
In ancient times, bronze casting is ideal for toolmaking(like tools and weapons). Historians believe true bronze artifacts(like cymbals) led to the creation of complex societies and trade networks.
Besides, metallurgy allowed ancient civilizations like Greece and China to flourish and leave lasting legacies in art, architecture, and warfare.
Composition of Bronze
Known as a metal alloy primarily composed of copper and tin, bronze is typically made up of around 88% copper and 12% tin.
However, the amount of each element can vary. Sometimes other elements such as aluminum, phosphorus, or silicon are also added to the mix to enhance certain properties, like strength, durability, and ductility.
The composition can also affect the color and appearance. Depending on the ratio of each element, the color can range from a reddish brown to a deep golden hue.
Properties of Bronze
Bronze has many unique and specific properties.
Strength and durability: You can regard it as a perfect material for outdoor applications.
Resistant to corrosion: This material is a long-lasting choice for architectural elements.
Low metal-to-metal friction: Works especially well in bearings and bushings.
Ductile and easier to cast: This ability allows intricate designs to be cast or molded. It’s a boon for artists who request a free to create detailed and intricate pieces with precision.
| Basic Attribution of Bronze |
| Alloy Composition | 88% Copper+12% Tin(Changeable) |
| Color | Reddish brown to deep golden hue |
| Properties |
|
Different Types of Bronze
Bronze includes many different types. When combined with other metals, this alloy yields different properties.
Let’s see several common bronze alloys.
Aluminum Bronze

Aluminum Bronze contains copper and a high percentage of aluminum, which increases its strength and corrosion resistance.
This type of bronze is used in marine applications and environments where corrosion is a concern.
Phosphor Bronze

Phosphor Bronze contains a small amount of phosphorus. This alloy has excellent wear resistance and high strength.
It is often used in musical instruments due to its ability to produce a clear and resonant sound.
Manganese Bronze

Manganese Bronze contains a high percentage of manganese, which improves its strength and hardness.
This type of bronze is used in industrial applications where a strong and durable material is required.
Silicon Bronze
![]()
Silicon Bronze is a type of bronze alloy that contains silicon as a main alloying element. It is known for its high strength, corrosion resistance, and good electrical conductivity.
This type of bronze is commonly used in marine hardware, sculptures, and musical instruments.
Bearing Bronze
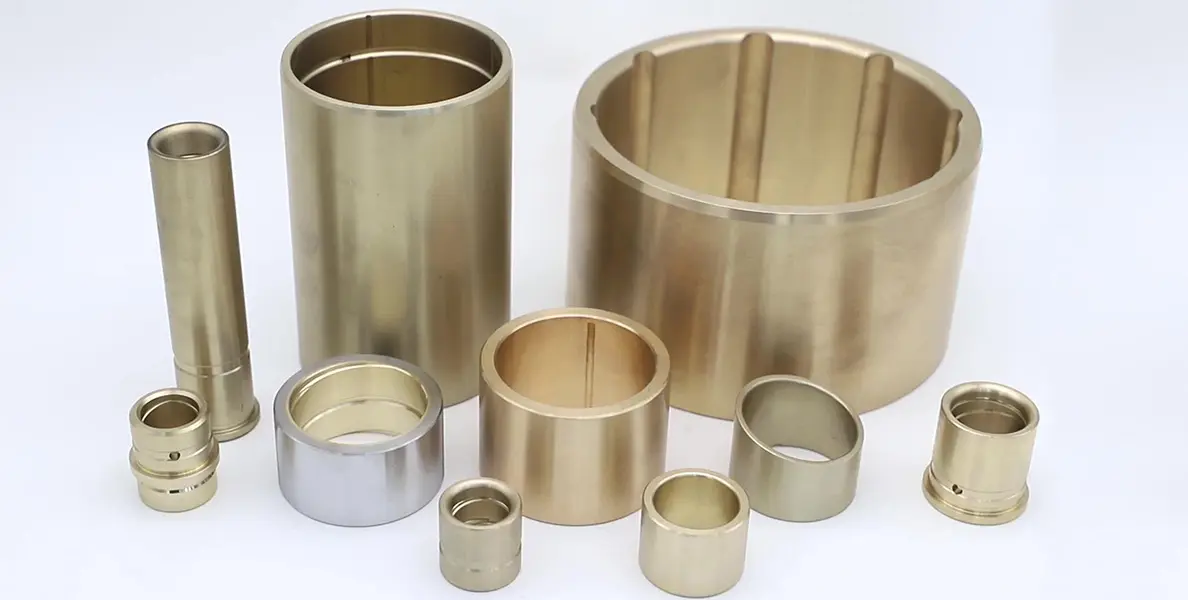

Bearing Bronze is a type of bronze specifically formulated for use in bushings and bearings.
This alloy typically contains a higher percentage of tin, which contributes to its self-lubricating properties. This property helps it with heavy machinery and equipment.
Other Types of Bronze

Other types of bronze incorporate different metals to create unique properties. Here are several examples.
Nickel bronze: Has a higher concentration of nickel in the alloy. This type is popular in marine applications and outdoor sculptures due to its durability and anti-corrosion ability.
Zinc bronze: It consists of a certain proportion of copper and zinc. This type has a lighter color. Manufacturers often use it in decorative applications like jewelry and architectural accents.
Leaded bronze: Contains a higher lead content. The lead provides excellent lubricity, reducing friction and wear in moving parts. This type is commonly used in heavy-duty components.
| Different Bronzes |
| Higher Content of Elements | Properties | Application |
| Aluminum |
|
|
| Phosphor |
|
|
| Manganese |
|
|
| Silicon |
|
|
| Tin(Bearing) |
|
|
| Nickel |
|
|
| Zinc |
|
|
| Lead |
|
|
Comparison of Bronze with Other Copper
In this part, We shall conduct a comparative analysis of the distinctive properties of this material to other types of copper.
Compare With Brass

The main difference between brass and bronze lies in the composition. Bronze is primarily made of copper and tin, while brass is a mixture of copper and zinc.
This leads to differences in the physical properties. Bronze is harder and more durable than brass. In terms of color, bronze tends to have a more reddish-brown hue while brass tends to be more yellowish.
| Attributions | Bronze | Brass |
| Main Composition apart from Copper | Tin | Zinc |
| Physical Properties | Harder | Softer |
| Color | Reddish-Brown | Yellowish |
Compare With Pure Copper

Bronze is a stronger and more corrosion-resistant material. The secret hides in the tin in bronze, which enhances its strength and durability.
Pure copper, on the other hand, is softer and more malleable. it works perfectly in electrical applications and related industries.
| Attributions | Bronze | Pure Copper |
| Corrosion Resistance | Better | Worse |
| Physical Properties | Harder and durable | Softer and malleable |
Compare With Copper-Nickel Alloy
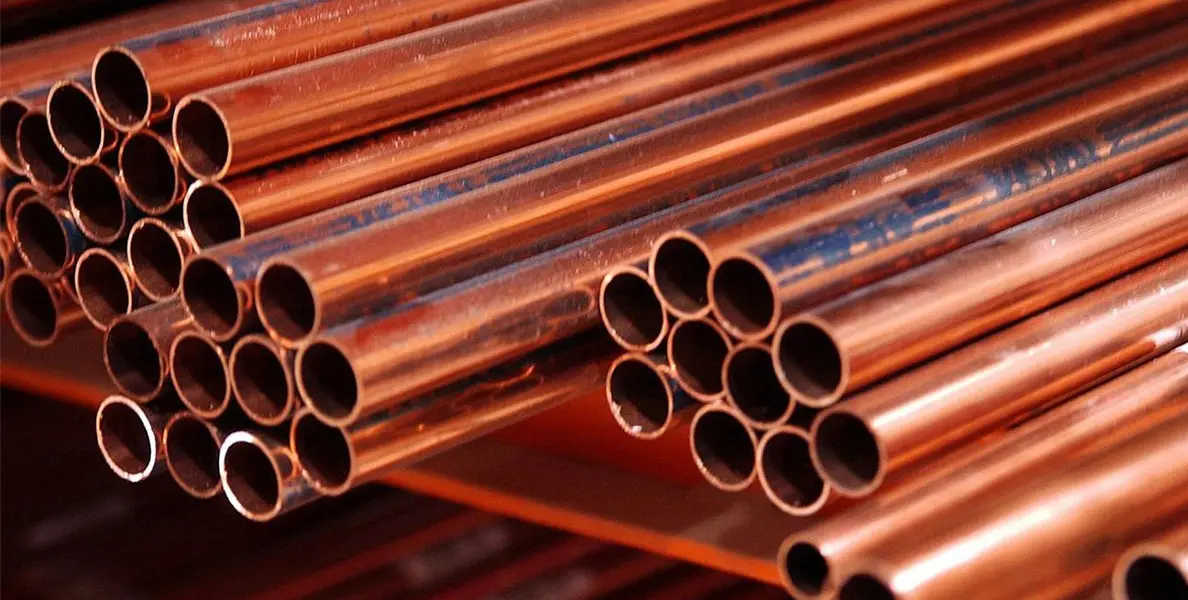

Bronze typically has a higher copper content. This material is often preferred for decorative purposes due to its more attractive appearance.
Copper-nickel alloys are known for their excellent resistance to seawater corrosion. This property makes it ideal for marine engineering applications.
| Attributions | Bronze | Copper-nickel alloys |
| Copper content | Higher | Lower |
| Appearance | More attractive | Less attractive |
| Anti-seawater corrosion | Worse | Better |
Modern Manufacturing Applications of Bronze
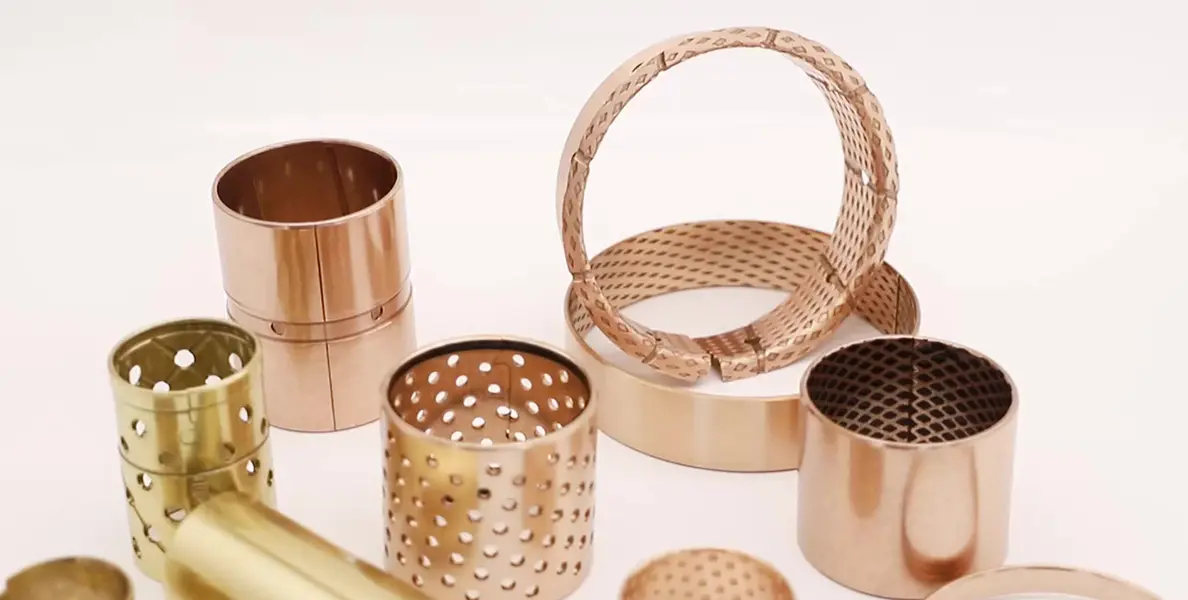

Bronze has a wide range of applications. In this part, let’s see how this material works in the aerospace, automotive, and architecture industries.
In the Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, bronze is used for a variety of applications due to its strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. Related parts include bearings, gears, and connectors.
Bronze components ensure the smooth operation of aircraft engines and other critical systems, making them an essential material in the aerospace sector.
In Automotive Manufacturing
Bronze components in automotive manufacturing are also widely used for durability and wear resistance.
From engine parts to suspension components, bronze withstands the harsh conditions of daily driving. Automotive manufacturers rely on bronze to create high-performance vehicles that can withstand the rigors of the road.
Decorative Use in Architecture
The decorative use of bronze in architecture has been a tradition for centuries. Bronze is used for applications like statues, sculptures, and ornaments adorning buildings.
The natural beauty combined with durability and malleability, makes bronze a popular choice for architectural embellishments that stand the test of time.
| Industry Field | Utilized Properties | Related Parts and Use |
| Aerospace |
|
|
| Automotive |
|
|
| Architecture |
|
|
Conclusion

Overall, bronze has significantly influenced industrial manufacture and the trajectory of human civilization.
The material exhibits a wide range of variations and possesses distinct characteristics. These properties result in a substantial influence on several domains of production and daily existence.
Where Can I Get Great Bronze Products?
You can contact with XMAKE! We are a leading digital manufacturing platform capable of handling a wide range of materials. On top of that, we can make the most cost-effective, top-notch products for you!
FAQS
Q1: Where is bronze commonly used?
A: Bronze is used in sculptures, ship propellers, machinery components, and musical instruments.
Q2: What is bronze disease? How can this disease be prevented?
A: Bronze disease is a type of corrosion that forms on bronze objects when exposed to chlorides. To prevent this disease, it is important to keep objects dry and avoid exposure to chloride-containing environments.
Q3: What do the Chinese call bronze?
A: Qing Tong, Qing for lime green(color when it rusts), Tong for copper in Chinese.
Q4: Where can I learn more about the history and significance of bronze?
A: You can find detailed information about bronze in encyclopedias like Britannica or through historical resources on metalworking and sheet metal fabrication.
References
- Bronze – Encyclopedia of China, 3rd online edition. (n.d.). https://www.zgbk.com/ecph/sublibrary?SiteID=1&ID=606
- Bronze alloy and copper performance and application differences – Xinkang material class research service platform. (n.d.). https://www.xk-materials.cn/newsView_239.html
- Tin bronze in the aviation industry in the application of the current situation and future development trend? _Baoding Da Ze Copper Co. (n.d.). http://www.dazety.com/news/1122.html